简介
flowable engine一共有5种:App, CMMN, DMN, Form, Process(即BPMN)。
flowable-spring-boot-starter提供了零配置集成flowable的功能,主要包括各类型engine的自动配置、流程/表单定义自动部署,其次还有rest-api,spring boot aucuator集成等。
这篇文章主要是解析flowable在spring boot环境下的启动流程,不涉及flowable内部原理。
flowable相关的AutoConfiguration
# flowable-spring-boot-autoconfigure: spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.flowable.spring.boot.environment.FlowableDefaultPropertiesEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.environment.FlowableLiquibaseEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Flowable auto-configurations
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.flowable.spring.boot.actuate.info.FlowableInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.EndpointAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.RestApiAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.app.AppEngineServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.app.AppEngineAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.ProcessEngineServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.FlowableJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.form.FormEngineAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.form.FormEngineServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.content.ContentEngineAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.content.ContentEngineServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.dmn.DmnEngineAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.dmn.DmnEngineServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.idm.IdmEngineAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.idm.IdmEngineServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.cmmn.CmmnEngineAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.cmmn.CmmnEngineServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.ldap.FlowableLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.flowable.spring.boot.FlowableSecurityAutoConfiguration
看起来比较多,不过大多数AutoConfiguration逻辑还是比较简单的。
engine自动配置
各engine的配置方式大同小异,以ProcessEngine为例,其涉及到的AutoConfiguration主要是
- ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration
- ProcessEngineServicesAutoConfiguration
ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration
ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration类图
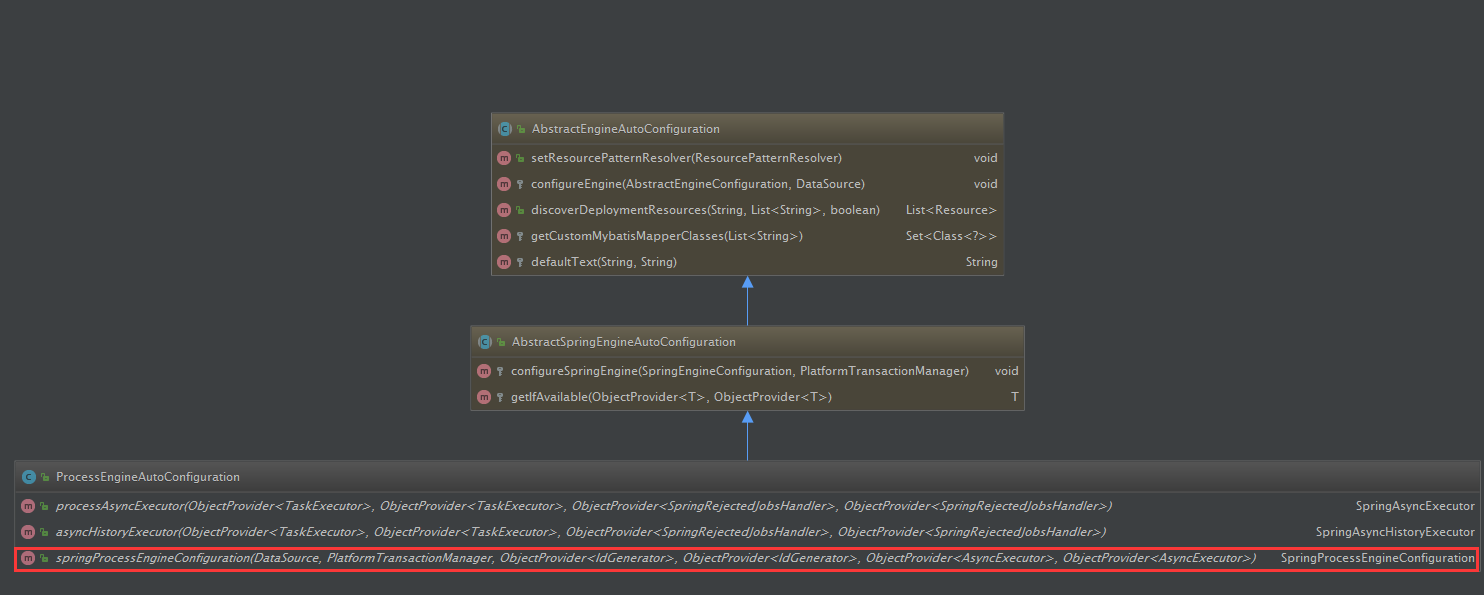
从红框部分可以看到,在ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration中配置了一个类型为SpringProcessEngineConfiguration的bean,其类图如下
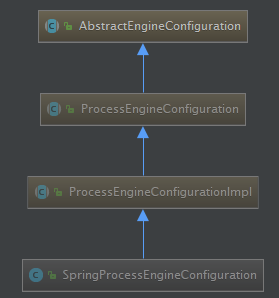
可知,SpringProcessEngineConfiguration是ProcessEngineConfiguration的子类,而ProcessEngineConfiguration正是用于创建ProcessEngine的类。
不过这里只是注册了一个bean,并没有调用其buildProcessEngine()方法来创建ProcessEngine。ProcessEngine实例是在ProcessEngineFactoryBean中创建的。
ProcessEngineServicesAutoConfiguration
这个AutoConfiguration主要负责配置ProcessEngineFactoryBean及各个Service(RuntimeService, RepositoryService, TaskService等)。
各Service的配置比较简单,主要来看看ProcessEngineFactoryBean
ProcessEngineFactoryBean
需要注意的是ProcessEngineFactoryBean是在内部类ProcessEngineServicesAutoConfiguration#StandaloneEngineConfiguration中注册的。
这是一个FactoryBean,我们知道Spring通过FactoryBean的getObject()方法来创建bean,来看看其代码
// ProcessEngineFactoryBean.java
public class ProcessEngineFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<ProcessEngine>, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
protected ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration;
@Override
public ProcessEngine getObject() throws Exception {
// 省略无关代码...
this.processEngine = processEngineConfiguration.buildProcessEngine();
return this.processEngine;
}
}
可以看到,ProcessEngineFactoryBean通过调用processEngineConfiguration.buildProcessEngine()创建了ProcessEngine的实例。
对于processEngineConfiguration这个对象的构建,可以参考ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration
自动部署
flowable spring boot starter能够自动将classpath的相关目录(如processes, forms)下的资源自动部署。
不同的engine逻辑大同小异,以ProcessEngine为例,其核心在于SpringProcessEngineConfiguration这个类。
SpringProcessEngineConfiguration实现了spring的SmartLifecycle接口,相关代码如下
// SpringProcessEngineConfiguration.java
@Override
public void start() {
synchronized (lifeCycleMonitor) {
if (!isRunning()) {
// 遍历engines实例进行部署
enginesBuild.forEach(name -> autoDeployResources(ProcessEngines.getProcessEngine(name)));
running = true;
}
}
}
@Override
public void stop() {
synchronized (lifeCycleMonitor) {
running = false;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isRunning() {
return running;
}
其中start方法正是对process engines所需要的资源进行自动部署,会在spring应用完成初始化后进行回调。
来看看autoDeployResources方法
// SpringProcessEngineConfiguration.java
protected Resource[] deploymentResources = new Resource[0];
protected void autoDeployResources(ProcessEngine processEngine) {
if (deploymentResources != null && deploymentResources.length > 0) {
final AutoDeploymentStrategy strategy = getAutoDeploymentStrategy(deploymentMode); // 选择部署策略
strategy.deployResources(deploymentName, deploymentResources, processEngine.getRepositoryService());
}
}
字段deploymentResources的值是关键,通过调试,发现该字段是在ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration中进行赋值的
// ProcessEngineAutoConfiguration
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SpringProcessEngineConfiguration springProcessEngineConfiguration(DataSource dataSource, PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager,
@Process ObjectProvider<IdGenerator> processIdGenerator,
ObjectProvider<IdGenerator> globalIdGenerator,
@ProcessAsync ObjectProvider<AsyncExecutor> asyncExecutorProvider,
@ProcessAsyncHistory ObjectProvider<AsyncExecutor> asyncHistoryExecutorProvider) throws IOException {
SpringProcessEngineConfiguration conf = new SpringProcessEngineConfiguration();
// 根据配置的规则找到相关的资源
List<Resource> resources = this.discoverDeploymentResources(
flowableProperties.getProcessDefinitionLocationPrefix(),
flowableProperties.getProcessDefinitionLocationSuffixes(),
flowableProperties.isCheckProcessDefinitions()
);
if (resources != null && !resources.isEmpty()) {
conf.setDeploymentResources(resources.toArray(new Resource[0]));
conf.setDeploymentName(flowableProperties.getDeploymentName());
}
// ...省略无关代码
return conf;
}
TODO LIST
- List<EngineConfigurationConfigurer>